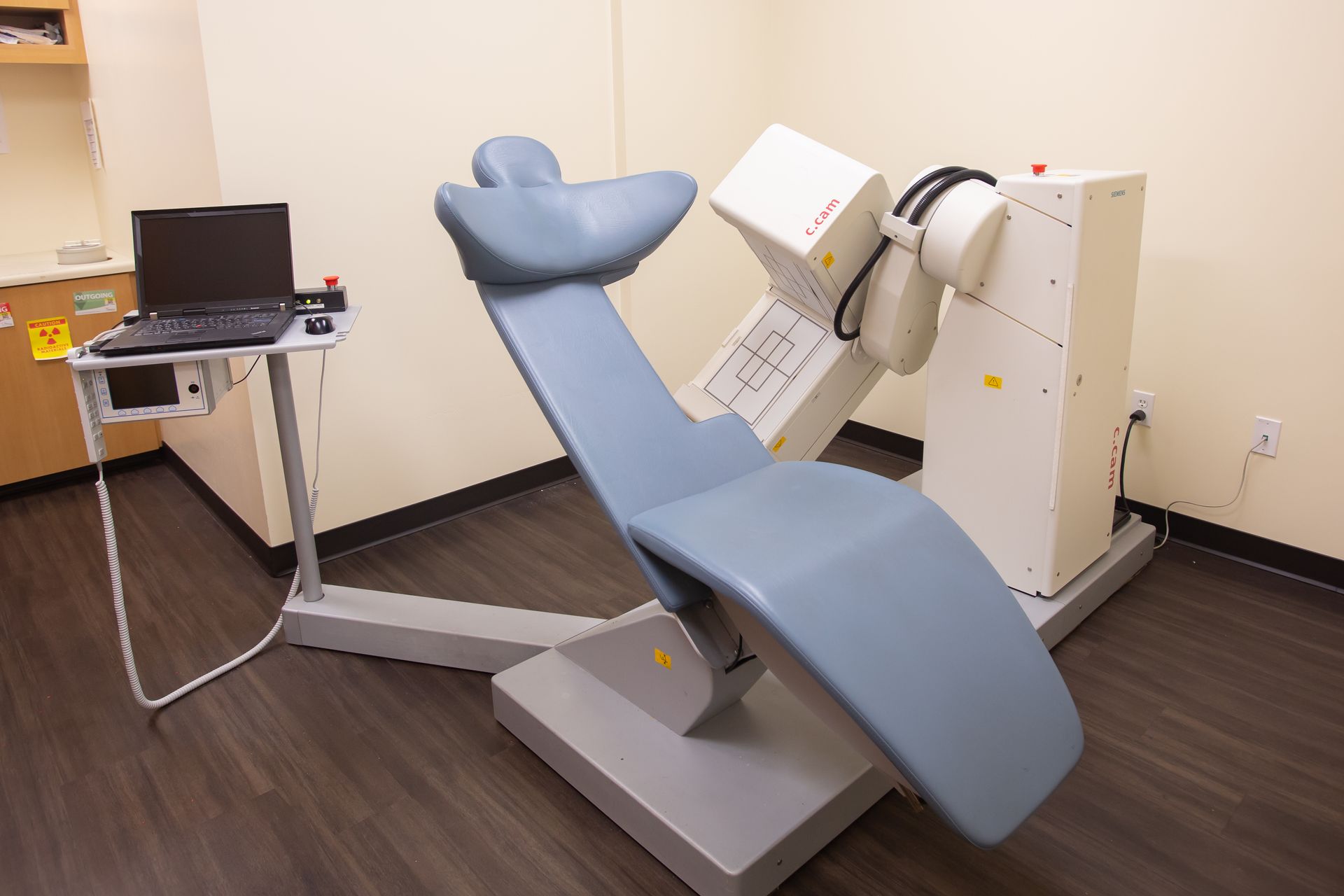
San Diego Heart and Vascular Associates
An Association of Independent Physicians
In Office Testing
Myocardial Perfusion Imaging (Nuclear Stress Test)
This is a 3 hour test involving injection of a small amount of harmless radioactive substance (Myoview) to assess blood flow to different regions of the heart muscles. The test assists us in detecting significant coronary artery disease by imaging the uptake of the radioisotope.
Patients determined to need Myocardial Perfusion Stress Test as part of their workup for coronary artery disease will be given special instructions in the office.
For more information on Nuclear Cardiology please visit www.radiologyinfo.org
Technetium Pyrophosphate Studies
A Technetium Pyrophosphate (Tc-PYP) exam is a diagnostic test used to detect and evaluate heart conditions, particularly related to the heart muscle. When you go to a doctor for a Tc-PYP exam, here's what you can generally expect:
During the exam, a small amount of Technetium-99m Pyrophosphate, a radioactive tracer, will be injected into your vein. This tracer is designed to attach to damaged heart muscle cells.
Waiting period: After the injection, you will typically need to wait for a certain period, usually around 3 hours. This waiting time allows the tracer to distribute throughout your body and concentrate in the heart muscle.
Imaging: Once the waiting period is over, you will undergo a specialized imaging procedure, such as a single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) scan. This involves lying down on a table while a gamma camera rotates around you, capturing images of your heart. The camera detects the radioactive tracer and creates detailed pictures of your heart's structure and function.
Comfort and safety: Throughout the entire process, medical professionals will ensure your comfort and safety. They will be available to answer any questions or address any concerns you may have.
Follow-up: After the imaging is complete, the images will be interpreted by a cardiologist. The findings from the Tc-PYP exam will help guide your doctor in diagnosing and planning the appropriate treatment for your heart condition.
Your healthcare team will inform you of any specific precautions to take and will closely monitor you throughout the procedure.

Echocardiogram
An echocardiogram is a non-invasive procedure that uses sound waves (ultrasound) to evaluate how well the heart is working. Gel is applied to the chest and a transducer (wand-like apparatus) is moved over the chest area to produce an image of the internal structures of the heart.
The test will take from 30-60 minutes depending on the patient’s condition and the type of echo that is ordered by the doctor.
Why is an echocardiogram done?
An echocardiogram will help the doctor to evaluate:
- How well the heart is moving
- How well the valves are working
- The size of the heart and it’s pumping chambers (ventricles)
What preparation is needed for the test?
- There are no restrictions on food, liquids or medications for this test
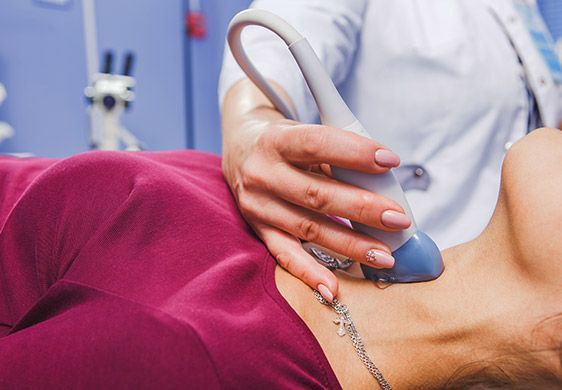
Carotid Doppler Ultrasound
A Carotid Doppler ultrasound is a painless procedure that measures the amount of blood flow in the carotid arteries. The carotid arteries are the two major arteries on each side of the neck that carry blood to the head.
The Doppler takes about 30-45 minutes. The technician will place a clear gel on the side of your neck. She will then use a sensor that looks like a wand to get an ultrasound image of rate of blood flow through your carotid arteries. Any narrowing of the arteries will show up as an area of reduced blood flow.
Why is a carotid Doppler done?
- Carotid Doppler scanning is used to evaluate the risk of stroke in patients who have a history of stroke or are at high risk.
What preparations are needed?
- No special preparations are needed for this procedure.
Upper and Lower Extremity Arterial doppler Studies
An Arterial ultrasound uses sound waves at a frequency that is higher than humans are able to hear to produce images on a monitor for the purpose of evaluating the arterial blood flow to the upper and lower extremities.
The procedure takes between 45-60 minutes.
Why is this test ordered?
The arterial ultrasound is able to demonstrate blocked or reduced blood flow through the major arteries of the arms and legs. It is used to evaluate:
- Numbness and tingling sensations in the hands, arms, feet and legs
- Sensation of fatigue and heaviness in the arms or legs
- To investigate the possibility of thoracic outlet syndrome
What preparations are needed?
- No special preparations are needed for this test.

Peripheral Vascular Ultrasound
A Peripheral Vascular ultrasound is a noninvasive peripheral vascular study that creates images of the body's blood vessels using sound waves. A small probe called a transducer emits high-frequency sound waves and sends the waves that bounce back to a computer which uses them to create an image.
The procedure takes between 45-60 minutes.
Electrocardiograph (EKG or ECG)
Electrocardiography (ECG or EKG) is a transthoracic interpretation of the electrical activity of the heart over time captured and externally recorded by skin electrodes.
It is a noninvasive recording produced by an electrocardiographic device. The etymology of the word is derived from electro, because it is related to electrical activity, cardio, Greek for heart, and graph, a Greek root meaning "to write".
Electrical impulses in the heart originate in the sinoatrial node and travel through the intimate conducting system to the heart muscle. The impulses stimulate the myocardial muscle fiber's to contract and thus induce systole. The electrical waves can be measured at electrodes placed at specific points on the skin. Electrodes on different sides of the heart measure the activity of different parts of the heart muscle. An ECG displays the voltage between pairs of these electrodes, and the muscle activity that they measure, from different directions, can also be understood as vectors. This display indicates the overall rhythm of the heart and weaknesses in different parts of the heart muscle. It is the best way to measure and diagnose abnormal rhythms of the heart, particularly abnormal rhythms caused by damage to the conductive tissue that carries electrical signals, or abnormal rhythms caused by electrolyte imbalances.
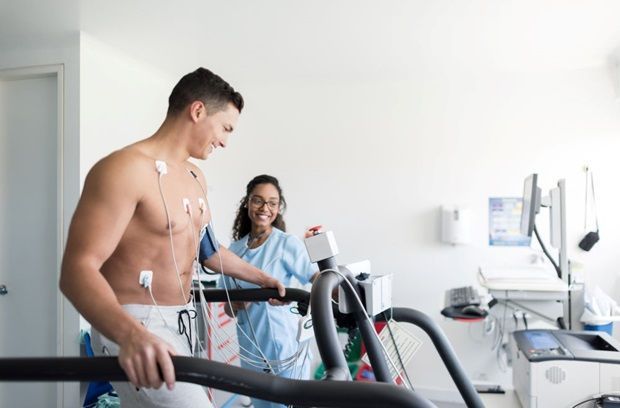

Exercise Stress Test / Treadmill Test
What is an Exercise Treadmill Test?
Electrodes are placed on the chest to monitor the heart’s rate and rhythm throughout the test. The cardiologist will have the patient walk on a treadmill, gradually increasing the speed and incline. The patient will exercise from a few minutes up to fifteen minutes depending upon the patient’s level of ability. The test will be stopped if the patient becomes too tired or has symptoms such as chest pain. The cardiologist will be looking for changes in the EKG pattern and any symptoms that the patient may experience. At the peak of exercise, the treadmill will be stopped, and the patient will be instructed to lie down immediately on an exam table.
What preparation is needed?
- Please do not eat a heavy meal before testing
- Wear comfortable clothing (shorts/pants with shirt/ blouse) and walking/jogging shoes
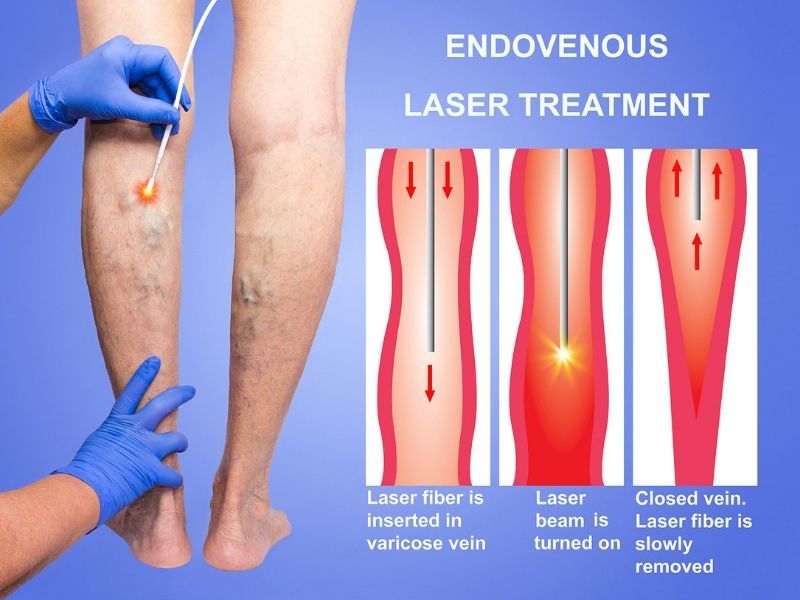
Endovenous Laser Treatment
Lasers have been used for numerous medical applications throughout the body. Recently, a novel technique utilizing laser energy delivered endovenously (directly inside the vein) has been developed to treat varicose veins. An 810mm diode laser will be used to deliver the laser energy via a small laser fiber.
Endovenous Laser Treatment is performed under local anesthesia in the doctor's office. There is little to no scarring and it has a relative short recovery period after the procedure. This is an outpatient procedure, which means you can resume your normal activities almost immediately.
During the procedure, you will be given special eye goggles to protect your eyes against accidental exposure to laser light. Next, the treatment area will be anesthetized with a common anesthetic, Lidocaine. A sterile fiber will be inserted into the vein and positioned under ultrasound guidance. Laser energy will be delivered to selectively treat the target vein. a compression stocking will be applied.
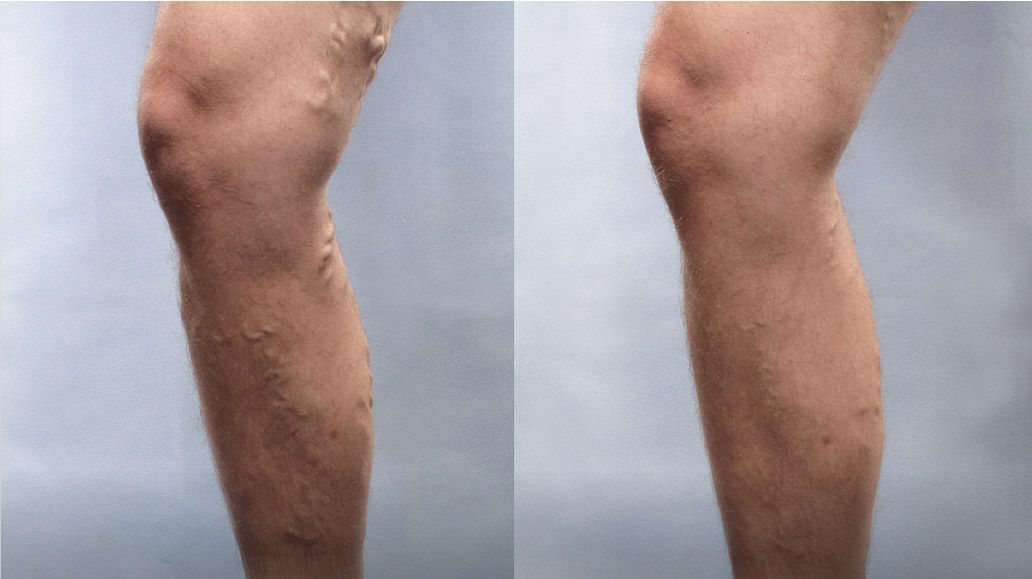
Varithena Procedure
Varithena Vein treatment involves injecting a microfoam that causes veins to close. Varithena procedures are minimally invasive. There's no need for incisions or stitches, and treatment is usually less than an hour.
Varithena is a non-thermal, non-tumescent treatment for the great saphenous vein system (GSV) and associated veins of the GSV system, and is a foam indicated for treating venous insufficiency.
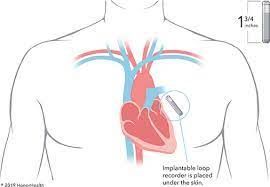
Loop Recorder Implantation
What is loop recorder implantation?
An implantable loop recorder, or ILR, is a heart recording device that is implanted in the body underneath the chest skin. It has several uses. The most common ones include looking for causes of fainting, palpitations, very fast or slow heartbeats, and hidden rhythms that can cause strokes. During a loop recorder implantation, your heart healthcare provider (cardiologist) does a minor procedure. He or she places the small device under your skin, on your chest wall, overlying the heart. The machine works as an electrocardiogram (ECG), continuously picking up electrical signal from your heart.
This can help find abnormal heart rhythms that can cause a number of problems such as fainting.
Normally, a special group of cells begin the electrical signal to start your heartbeat. These cells are in the sinoatrial (SA) node. This node is in the right atrium, the upper right chamber of your heart. The signal quickly travels down your heart’s conducting system to the ventricles. These are the 2 lower chambers of your heart. As it travels, the signal triggers nearby parts of your heart to contract. This helps your heart pump blood in a coordinated way.
Any disruptions to this signaling pathway may result in heart rhythm problems. These might cause a number of problems, such as fainting and palpitations. An abnormal heart rhythm (arrhythmia) may make your heart unable to pump as much blood as needed. The temporarily reduced blood to your brain is what causes you to faint. When the rhythm returns to normal, you normally regain consciousness.
Each heart rhythm problem may need its own treatment. It’s important to find out what kind of problem you may have, if any. An implantable loop recorder continuously records information about your electrical activity, similar to an ECG. However, an implantable loop recorder can record heart rhythm for up to 3 years. It is continuously looping its memory and has automatic triggers to store recordings. It can also be patient activated to store recordings as well. If you fainted due to an arrhythmia, the machine records this information before, during, and after the fainting. Then a healthcare provider can look at the recordings to figure out the cause.
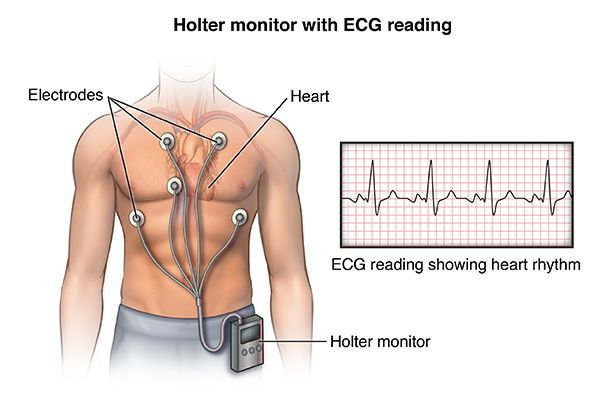
Holter Monitor
A Holter monitor is a portable device for continuously monitoring the electrical activity of the heart for 24 to 48 hours. Its extended recording period is sometimes useful for observing occasional cardiac arrhythmias that would be difficult to identify in a shorter period of time. For patients having more transient symptoms, a cardiac event monitor which can be worn for a month or more can be used. Much like standard electrocardiography (ECG), the Holter monitor records electrical signals from the heart via a series of electrodes attached to the chest. The number and position of electrodes varies by model, but most Holter monitors employ from three to eight. These electrodes are connected to a small piece of equipment that is attached to the patient's belt, and is responsible for keeping a log of the heart's electrical activity throughout the recording period.
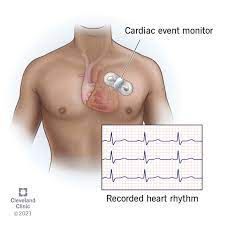
Telemetry Monitors and Event Monitors
What are heart rate monitors?
Heart rate monitors are devices that detect and measure your heart or pulse rate. Thanks to advances in technology, these devices are small, wearable and many use sensors that are very accurate. However, while these devices are excellent for personal use, they’re no substitute for medical devices that are much more accurate.
Why do people use heart rate monitors?
Heart rate monitors are very popular features in wearable devices like smartwatches and fitness trackers. Many of these devices also connect wirelessly to smartphones and computers. That allows users easy access to review their heart rate data. Heart rate monitors see common use for the following purposes:
- Tracking heart rate during exercise.
- Monitoring stress and activity levels during the day.
- Tracking sleep quality at night.
Monitoring your vital signs at home, especially if you have certain health conditions or concerns.

Ankle Brachial Index
The ankle brachial index, or ABI, is a simple test that compares the blood pressure in the upper and lower limbs. Health care providers calculate ABI by dividing the blood pressure in an artery of the ankle by the blood pressure in an artery of the arm. The result is the ABI.
In peripheral artery disease, plaque builds up in the arteries. It often affects the vessels that bring blood to the legs. The reduced blood flow can cause pain and numbness. Low ABI may mean that your legs and feet aren’t getting as much blood as they need. An ABI test won’t show exactly which blood vessels have become narrowed or blocked, though.
During an ankle brachial index test, you lie on your back. A technician takes your blood pressure in both of your arms using an inflatable cuff, similar to the one used in the doctor’s office. The technician also measures the blood pressure in the ankles. The doctor uses these values to compute your ABI.

24 hour ambulatory blood pressure test
Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring is a way of measuring and managing high blood pressure.
Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring records your blood pressure (BP) readings over a 24-hour period, whether you’re awake or asleep. This happens outside your healthcare provider’s office, as you go about your daily life. You wear a cuff on your arm and a small device attached to a strap or belt.
Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring takes dozens of readings over a continuous period. In most cases, the device records readings every 15 to 30 minutes during the day and every 60 minutes at night. The device also measures your heart rate (how fast your heart is beating). Your provider uses this data to calculate your average BP over the 24-hour period. They also calculate changes in BP and heart rate, BP distribution pattern and other statistics.
Why is ambulatory blood pressure monitoring used?
Healthcare providers use this method for many reasons, including to:
Confirming a diagnosis of hypertension.
Identify how changes in your blood pressure relate to your daily activities and sleep patterns.
See how well your blood pressure medication is controlling your high BP.
Your medication may not control your BP throughout the entire day and night. Your provider may need to adjust your dosage or the times that you take your pills, depending on your BP patterns. Or, you may need more than one drug to stabilize your BP.
Identify changes in your blood pressure readings at your healthcare provider’s office versus at home.
These changes can help show your level of risk for cardiovascular disease.
Our Mission
At San Diego Heart and Vascular Associates our mission is to improve the health of our community while providing excellent quality care to patients in a safe environment where people work together at their full potential to make a positive change.
SERVICES
Hospital Therapies
In Office Testing
QUICK LINKS
CONTACT
San Diego Office
619-297-0014
501 Washington St
Suite 512
San Diego, CA 92103
Coronado Office
619-435-1660
OFFICE HOURS
Monday - Friday: 8am - 5:30pm
Saturday - Sunday: Closed